Aisin Revs Up in Endurance Races to Hone Electrification Technology
Jan.14, 2022

Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), battery electric vehicles (BEVs), and other eco-friendly vehicles are currently in production by a variety of manufacturers and are commonly seen on the roads today. But the advanced technologies used in these vehicles may have originated in motor sports.
In pursuit of excellence in electrification technology through racing, Aisin revved up its research in 2007 as it entered the FIA World Endurance Championship (WEC), known as one of the most cutting-edge motorsports that demands the best in automotive technologies.
What is the FIA World Endurance Championship (WEC)?
The WEC is a world championship governed by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA), and is recognized as the world's highest level of motor racing, along with F1 (*1) and WRC (*2).
The event is known as the pinnacle of endurance racing, and in order to win, vehicles must be both fast and strong enough to drive safely over a long stretch of time and distance.
In the WEC, eight (*3) races are held during the season, one of the most famous and important being the 24 Hours of Le Mans, in France. It is the most grueling race in the world, with almost a century of history and tradition, and only the bestcar manufacturers have provided the technological capabilities required to win this prestigious competition.
*1: FIA Formula One World Championship
*2: FIA World Rally Championship
*3: Reduced to six races in 2020 and 2021 due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Lapping Competitors in Technology Development Capabilities through Racing
Automobile manufacturers and parts suppliers actively take part in racing to develop their technologies. In races, cars are driven close to their limits for long stretches of time, causing many problems that would not normally occur in normal, day-to-day driving. There is no better environment for testing and refining new technologies, and many of the advancements discovered through racing have been adopted into production vehicles. In its continuing pursuit of excellence, Aisin is using motorsports as a starting point to further develop its electrification technology, which has been gaining increasing interest.
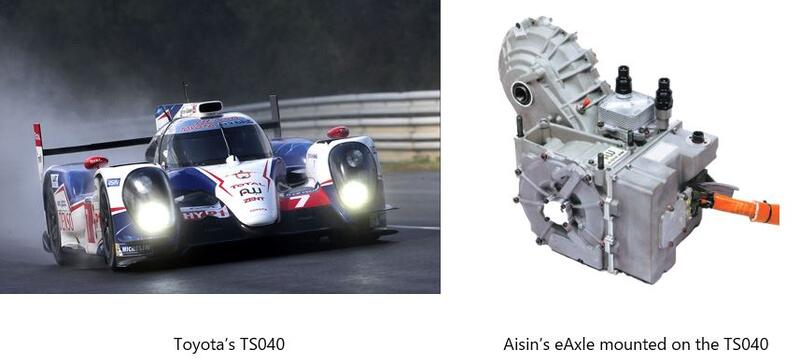
Aisin's Development of an eAxle for Racing and Competing in the WEC
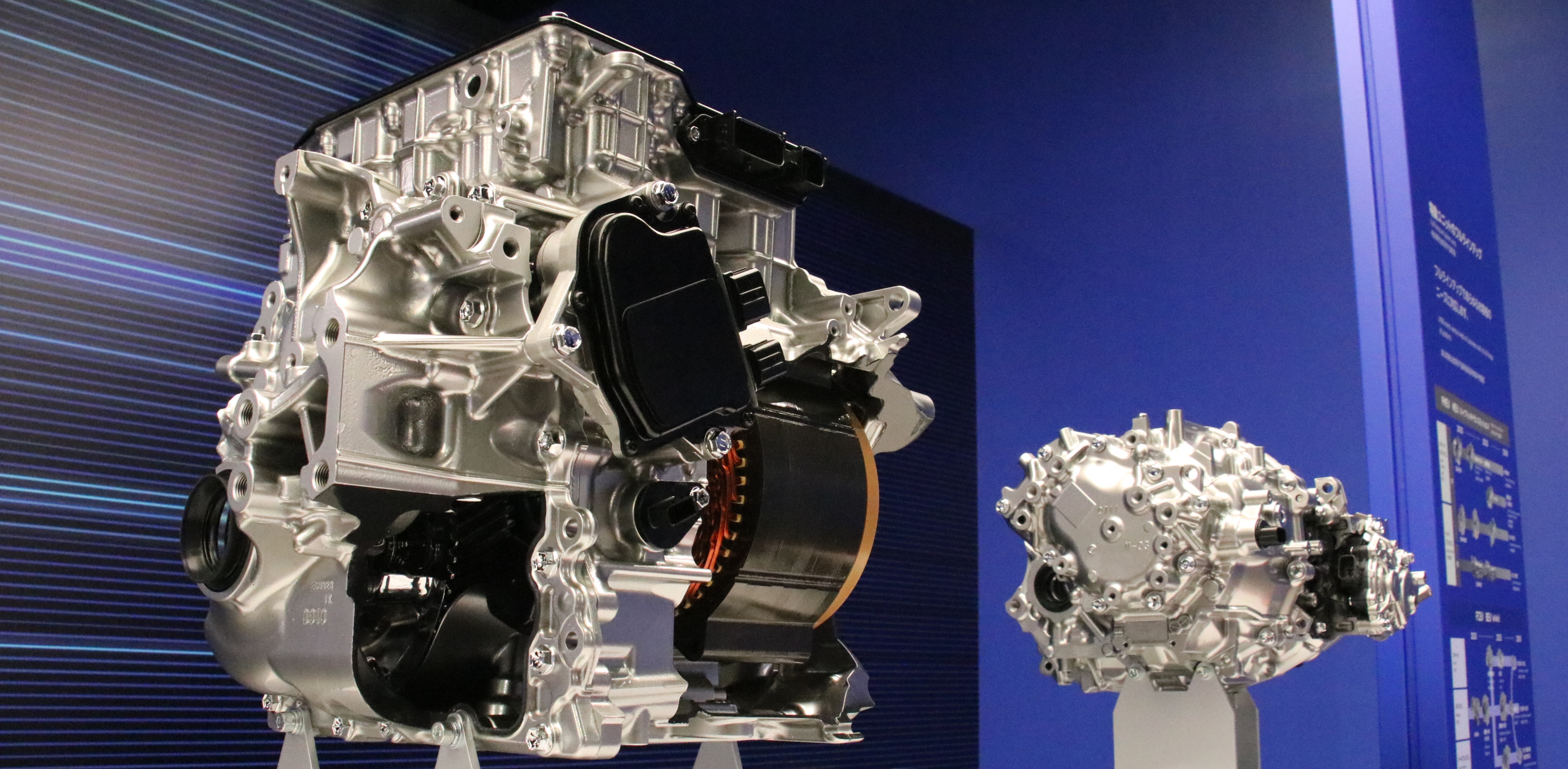
Aisin's development of an eAxle for racing began with the 2007 Tokachi 24 Hours. An eAxle is a drive unit that integrates the motor, the gearbox, and the inverter. We provided the Toyota Supra HV-R with a motor for the rear wheel, which was made lighter by reviewing the design from the ground up, including the materials, down to the nearest 0.1 g. This greatly contributed to the victory in the race.
In 2008, Aisin took charge of the development of an eAxle for the front wheel of the TS030, Toyota's first hybrid car as a prototype racing car. An eAxle for the front wheel must be developed with a motor, gearbox and inverter as a set so that it can be mounted in the front of the vehicle where space is limited. Aisin believed its strength in integration technology could be utilized in this development, and this challenge was also in anticipation of the development of next-generation technologies for the age of electrification.
Through much trial and error, Aisin succeeded in creating a highly efficient motor system that is ultra-compact and lightweight, achieving a power-to-weight ratio (*4) 10 times that of mass-produced systems. Unfortunately, due to a sudden change in the regulations of the WEC, the eAxle could no longer be mounted, and was forced to leave the front line.
Yet Aisin ceaselessly continued development and in 2014, Aisin’s eAxle was finally included in the TS040 and made its WEC debut.
*4: Power output per kilogram of unit mass (power / unit mass)
Le Mans and a Long-Awaited Victory
Aisin’s eAxle showed tremendous power throughout the WEC series. The Toyota Racing team won the 2014 championship in the TS040, but was unable to reach its longstanding goal of winning the 24 Hours of Le Mans. The team tried again in 2015, but its rivals significantly improved their performance and the Toyota team was utterly defeated. Taking this defeat as an opportunity, Aisin took on the challenge of developing a new eAxle with new technologies.
The next few years were a series of lessons and hardships. Every time the Aisin team members encountered a problem, they made improvements and took on the challenge of creating new technology, while thoroughly pursuing quality. Although the development process was extremely difficult, this experience helped produce a great leap forward in Aisin's electrification technology.
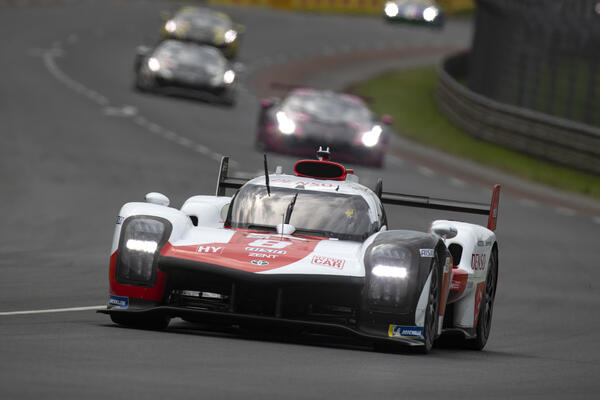
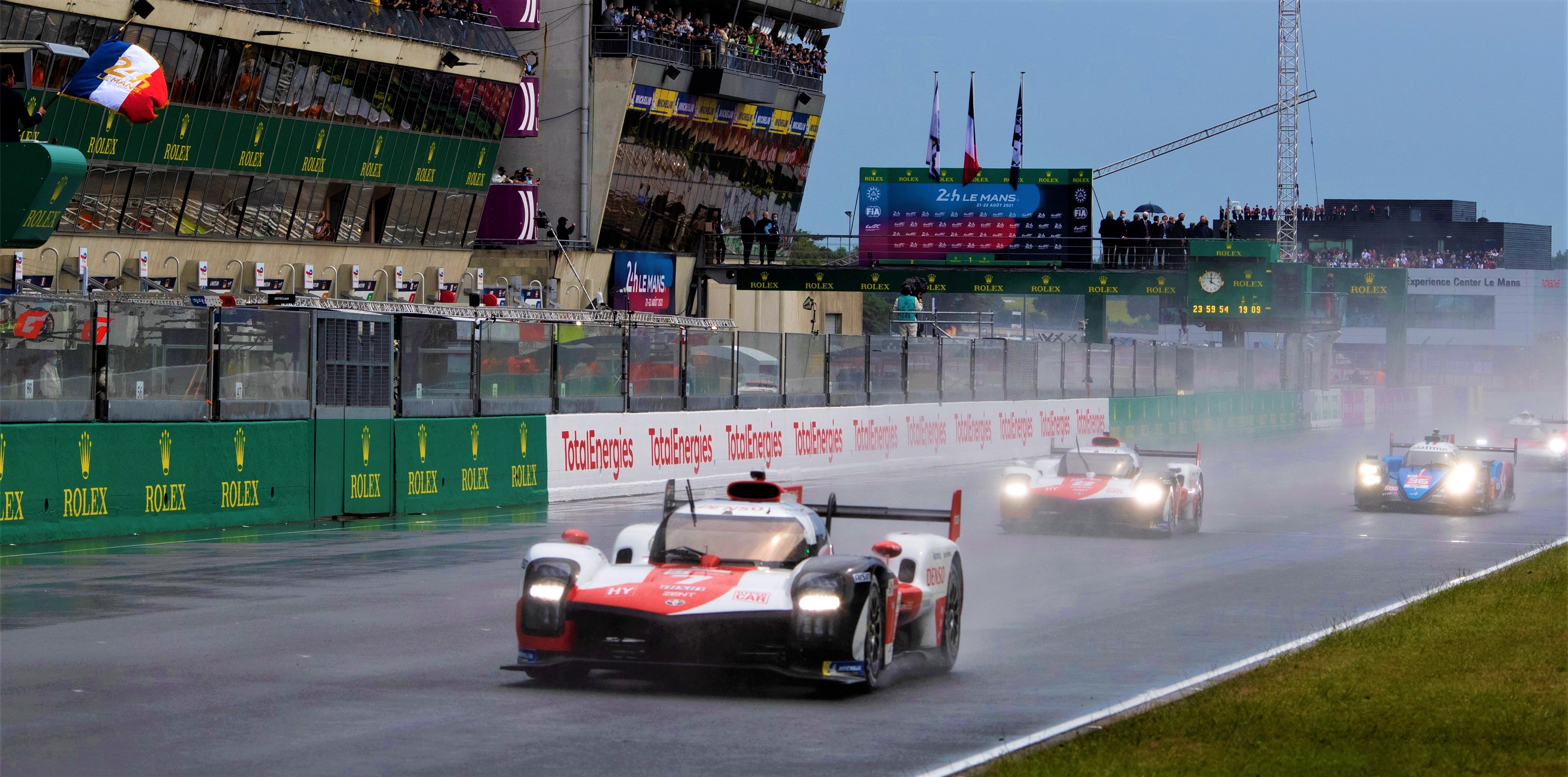
In 2018, four years after its first attempt at Le Mans, the Toyota Racing team showed stable performance from the beginning of the race to the end in a TS050 equipped with the new eAxle which enhanced torque, power and quality, and finally achieved the long-anticipated dream of winning the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
The team showed overwhelming strength in the TS050 in 2019 and 2020 to clinch the victory. In 2021, the team used the new GR010, a car that was developed in accordance with the new regulations, and won the race, becoming the fourth consecutive winner at Le Mans. Aisin was pleased to be able to significantly contribute to this incredible achievement.
Toyota "GR010"
As momentum for carbon neutrality grows around the world, the demand for electric vehicles is rapidly increasing as a means of achieving this goal. Utilizing the technologies it has accumulated through motor sports, Aisin has been developing highly efficient and compact electric drive units, including the eAxle, to achieve the global goal of carbon neutrality.