Convert CO₂ into Power! Aisin's "Resource Recycling System" Begins Operation
Jul.05, 2023
Aisin is accelerating its efforts to achieve carbon neutrality(CN)in both production and products so that future generations can live with peace of mind in a sustainable society.
On the production side, we are promoting technological development focusing on reduction in power sources, heat sources and waste, clean energy, and resource recycling aimed at zero waste. One of the key outcomes of these intiatives is the resource recycling system at our Nishio Die-Casting Plant(Nishio City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan).
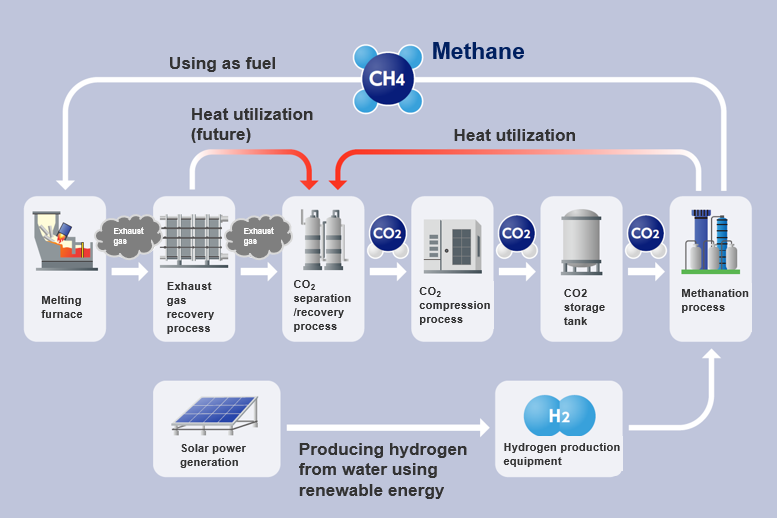
The resource recycling system separates, recovers and utilizes CO₂ contained in exhaust gas generated by combustion facilities at the plant. It produces methane gas from the recovered CO₂ to be circulated as fuel for melting furnaces. Our talented team members continually look for new ways to improve upon our activities and systems in order to reach our goal of production CN by 2035.
Why Aisin is making efforts to utilize CO₂
Aisin deals with a large number of automotive parts and components made from aluminum, including our industry-leading transmissions as well as new innovations such as the eAxle.
Aluminum melting furnaces and other combustion facilities primarily use energy from city gas. During combustion, CO₂ is emitted, accounting for about one-fourth of the plant’s CO₂ emissions. Due to the large amount of CO₂ emitted in the production process, realization of CN is a primary social responsibility and early establishment of carbon recycling technology is an urgent issue.
As one of its most promising solutions, Aisin launched a development project for the resource recycling system in July 2021. In less than two months, system evaluations were underway.
How the resource recycling system works
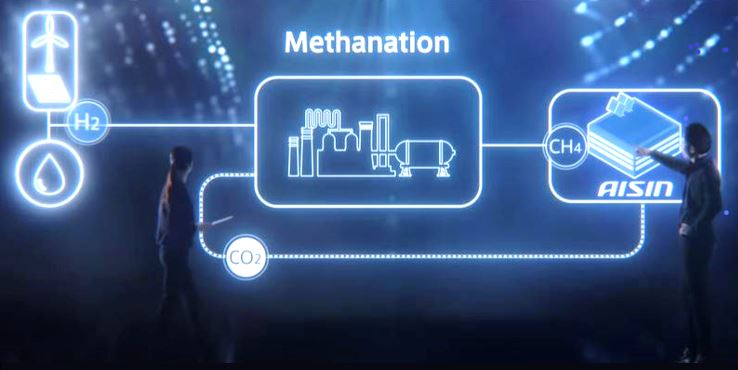
The resource recycling system consists of a process that separates and recovers CO₂ from exhaust gas generated by combustion facilities at the plant as well as a methanation process that produces methane gas- the main component of natural gas(LNG)- from the recovered CO₂.
High-temperature exhaust gas is emitted from aluminum melting furnaces at the plant in the gas recovery process. As a first step, particulates are removed from the gas and it is cooled to room temperature.
The CO₂ concentration at this stage is only around 5 to 10%. In the subsequent CO₂ separation and recovery process, the CO₂ concentration is increased to 99%, and the highly pure CO₂ is compressed and stored in tanks. In the next methanation process, CO₂ reacts with hydrogen to produce methane. The methane is then poured into the existing gas path to be reused.
By repeating the cycle of recovering CO₂ from the exhaust gas and reusing the produced methane as fuel, CO₂ emissions can be significantly reduced.
Characterized by downsizing, high efficiency and heat utilization
“The key to the system is the unique CO₂ separation and recovery process,” explains Kotaro Mizuma, who is in charge of development.
“Aisin has employed the chemical absorption method, which uses an absorbent to separate and recover CO₂,” says Mizuma “Combining this method with the originally designed recovery mechanism and its most suitable absorbent improves the efficiency of CO₂ separation and recovery, enabling downsizing. Systems using the chemical absorption method generally require equipment approximately 20 meters high whereas our system is only about 3 meters high. We believe thatminiaturization and low-energy operation performance, which are the key elements for practical application, have opened the door to commercialization,” adds Mizuma.
As for the methanation process, it is important to note that not only is methane produced, but the resulting heat is also reused. The heat generated when CO₂ reacts with hydrogen is circulated to the CO₂ separation and recovery process and used to heat the absorbent. Future improvements to system efficiency include using waste heat from melting furnaces for the CO₂ separation and recovery process whichwill efficiently reuse the heat that would normally be discarded.
Speedy development with diverse members
The project bridged engineers from various departments across organizational boundaries. Electric pumps and heat management technologies used in automobiles are utilized for liquid circulation. System downsizing and streamlining is a specialty of the production and engineering department. Akikazu Matsumoto, who leads the development project, emphasized good teamwork, says, “We were able to work as one, crossing departmental boundaries, toward the single goal of CN. One of Aisin’s strengths is its broad range of manufacturing technologies and know-how, from metal processing to equipment and chemical systems. In true Aisin fashion, members from various backgrounds, including those from group companies and business partners, worked together and took steady steps to reach the evaluation stage in a short period of time.”
Visualization of problems
The amount of CO₂ recovered by the evaluated system is approximately 1/100 of the CO₂ generated by a single melting furnace. Based on the data obtained from this evaluation, we will develop a system that can recover all of the CO₂ generated from a single melting furnace by FY2025.
The amount of exhaust gas emissions from a plant varies depending on various factors such as break times and setup times, making it incredibly difficult to increase performance by a factor of 100 while maintaining overall efficiency. We are currently tracking a variety of information including pressure and temperature with sensors attached to the system. We will identify any issues that may arise in the pursuit of highly efficient and stable CO₂ recovery and reuse.
Responding to social needs in a variety of ways
The world is about to be transformed into a decarbonized society. Matsumoto, who expressed his enthusiasm for the project, says, “All members share the sense of fulfillment and responsibility of being involved in technologies to prevent global warming. Lowering production CO₂ emissions should also help to strengthen the competitiveness of our products. There are many companies, like Aisin, that use melting furnaces and have the challenge of reducing CO₂ emissions. We will contribute to society by developing technologies that can also help other companies reduce CO₂ emissions, with a view to introducing these technologies to our group companies in the future.”
Aisin is promoting multifaceted technological development, including hydrogen combustion equipment and CO₂ fixation to achieve CN in production by 2035 and zero CO₂ emissions in plants by 2040. We believe that having multiple options allows us to flexibly respond to changing social infrastructure, varying fuel costs, and other circumstances.
Aisin will continue to protect the global environment and promote technological development that can flexibly respond to social needs. AI Think will continue to report on Aisin’s initiatives.